Introduction
In the world of HVAC systems, Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) play a pivotal role in maintaining indoor comfort and efficiency. Whether you’re a building manager, HVAC professional, or just someone curious about the technology behind modern climate control, understanding RTUs is essential. This guide will take you from the basics of RTUs to advanced insights, ensuring you gain a complete picture of this critical component in commercial HVAC systems.
What is an RTU (Remote Terminal Unit)? A Beginner’s Guide
An RTU, or Remote Terminal Unit, is a type of packaged HVAC system typically installed on rooftops. It combines multiple functions, such as heating, cooling, and ventilation, in one compact unit. RTUs are widely used in commercial and industrial buildings because of their efficiency, reliability, and ability to integrate with modern control systems.
RTU HVAC Meaning
In HVAC, RTU stands for Remote Terminal Unit. It refers to a self-contained, rooftop-installed unit designed for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning purposes. Understanding the RTU HVAC meaning is essential for selecting and maintaining the right system for your building.
Key Features of RTUs:
- Self-contained unit
- Rooftop installation
- Suitable for medium to large commercial spaces
- Can include economizers for energy savings
RTU Definition in HVAC
The RTU definition in HVAC encompasses its role as an all-in-one system that simplifies climate control for large buildings. RTUs are designed to provide efficient and scalable solutions for diverse applications.
History and Evolution of RTUs in HVAC Systems
RTUs first gained prominence in the mid-20th century as a solution to simplify HVAC installations. Over the decades, they have evolved to incorporate advanced technologies such as variable-speed compressors, smart controls, and energy-efficient designs.
What Does RTU Mean in HVAC?
What does RTU mean? In HVAC, RTU refers to a Remote Terminal Unit, a crucial component that consolidates various HVAC functions into one unit. This integration reduces complexity and improves overall efficiency.
Components of a Remote Terminal Unit
Key components include:
- Compressor: Facilitates the refrigeration cycle.
- Coils (Evaporator & Condenser): Responsible for heat exchange.
- Fans: Ensure proper airflow.
- Filters: Maintain air quality.
- Control System: Manual or automated controls for system operation.

Image : RTU (Remote Terminal Unit).
How Does an RTU Work in an HVAC System?
Step-by-Step Process:
- Air Intake: Outdoor air is drawn into the unit.
- Filtration: The air passes through filters to remove particulates.
- Conditioning: Depending on the mode, air is heated or cooled.
- Distribution: Conditioned air is supplied to the building through ductwork.
- Exhaust: Stale indoor air is expelled.
RTU Airflow: From Intake to Supply
Understanding airflow is crucial for optimizing performance. Ensure ducts are properly sealed and filters are clean to maintain efficiency.
Types and Configurations of RTUs
Single-Packaged vs. Multi-Packaged RTUs
- Single-Packaged: All components in one enclosure.
- Multi-Packaged: Separate enclosures for flexibility.
RTUs with Economizers
Economizers help reduce energy consumption by utilizing outdoor air for cooling when conditions allow.
Hybrid RTUs
These combine traditional gas heating with electric heat pumps for improved efficiency and sustainability.
Installation and Setup
RTU Installation Checklist
- Site inspection
- Structural support assessment
- Proper electrical connections
- Duct sealing
- System testing
How to Properly Size an RTU
Undersizing or oversizing an RTU can lead to inefficiencies. Use load calculation tools to determine the right capacity.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incorrect duct design
- Skipping calibration steps
- Ignoring building insulation
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Preventive Maintenance Checklist
- Regularly replace filters.
- Inspect and clean coils.
- Check electrical connections.
- Test thermostat and sensors.
How to Diagnose Common RTU Issues
- Airflow problems: Check for clogged filters or obstructed ducts.
- Refrigerant leaks: Inspect coils for damage.
- Electrical failures: Verify control board and motor connections.
Efficiency and Optimization
Energy Efficiency Tips
- Use programmable thermostats.
- Regularly clean and maintain components.
- Upgrade to variable-speed motors.
RTU Zoning
Zoning allows you to control different areas of a building independently, enhancing comfort and efficiency.
Advanced Technology in RTUs
Smart RTUs and IoT Integration
Smart RTUs enable remote monitoring, diagnostics, and control, improving operational efficiency.
AI and Machine Learning
Predictive analytics can optimize maintenance schedules and detect issues early.
RTU Buying Guide
RTU Full Form in HVAC
RTU stands for Remote Terminal Unit in HVAC, highlighting its function as a centralized system for heating, cooling, and ventilation.
What to Look for When Buying an RTU
- Capacity and efficiency ratings
- Warranty and support
- Compatibility with existing systems
Top RTU Models for 2024
Include a comparison table of the best RTUs based on performance, cost, and features.
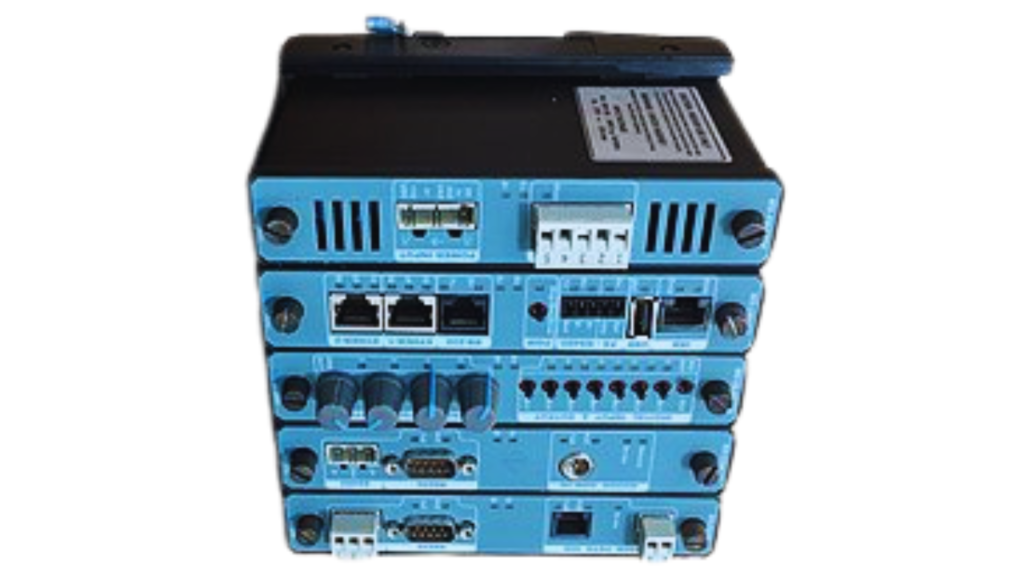

Image : Product images of top RTU models.
FAQs About RTUs
Common Questions Answered:
1. What is a Remote Terminal Unit (RTU)?
Answer:
A Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) is a device used in HVAC systems to monitor and control various equipment remotely. It collects data from sensors and systems, such as temperature and pressure, and sends it to a central control system. RTUs allow for efficient management of HVAC operations, reducing the need for manual intervention.
2. How does a Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) work?
Answer:
RTUs work by gathering data from connected HVAC devices, such as temperature sensors, humidity monitors, and pressure gauges. This data is sent to a centralized system, which can be accessed remotely for monitoring and control. RTUs often include control functions that allow operators to adjust HVAC settings from a distance.
3. What are the benefits of using an RTU in HVAC systems?
Answer:
- Remote Monitoring: Operators can access real-time data from anywhere, reducing the need for on-site visits.
- Energy Efficiency: By monitoring system performance remotely, RTUs help optimize energy usage.
- Proactive Maintenance: RTUs can send alerts for equipment malfunctions, enabling timely maintenance before costly failures.
- Reduced Downtime: Remote access allows for quick adjustments and troubleshooting, minimizing system downtime.
4. What are the components of a Remote Terminal Unit?
Answer:
RTUs typically consist of:
- Sensors: For measuring temperature, pressure, humidity, and other variables.
- Communication Interface: Allows data transmission to and from the central control system.
- Controller: Manages data collection, processing, and communication.
- Power Supply: Provides power to the RTU and its components.
5. Where are Remote Terminal Units used in HVAC systems?
Answer:
RTUs are commonly used in large commercial and industrial HVAC systems, including:
- Data Centers: For precise temperature and humidity control.
- Building Automation Systems (BAS): To integrate HVAC with other building systems for seamless control.
- Manufacturing Facilities: To monitor and control HVAC systems in critical environments.
6. What is the difference between RTU and a BMS (Building Management System)?
Answer:
An RTU is a device that monitors and controls HVAC equipment and sends data to a central system, whereas a Building Management System (BMS) is a comprehensive platform that integrates multiple systems, including HVAC, lighting, and security. RTUs are often part of a BMS, providing specific HVAC control and monitoring capabilities.
7. Can an RTU be integrated with other building systems?
Answer:
Yes, RTUs can be integrated with other building systems like lighting, security, fire alarms, and energy management systems. Integration allows for centralized control and optimization of all building functions from one platform.
8. What are the types of communication protocols used by RTUs?
Answer:
RTUs can use various communication protocols, including:
- Modbus
- BACnet
- LONWorks
- Ethernet/IP
- Wi-Fi or Cellular Networks (for remote communication) The choice of protocol depends on the specific requirements of the building or system.
9. How do RTUs improve energy efficiency in HVAC systems?
Answer:
RTUs provide real-time data and analysis of HVAC performance, which helps identify inefficiencies. They allow for adjustments based on environmental conditions or usage patterns, reducing energy consumption. Additionally, RTUs can optimize settings like temperature and humidity control to ensure efficient operation.
10. Are there any security concerns with using Remote Terminal Units?
Answer:
Since RTUs are often connected to the internet or local networks for remote access, there are potential security risks such as unauthorized access or cyberattacks. It is essential to implement robust security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and secure login protocols to protect RTUs from vulnerabilities.
11. What industries benefit the most from RTUs?
Answer:
Industries that benefit from RTUs include:
- Commercial Real Estate: For centralized HVAC control across multiple buildings.
- Data Centers: To maintain precise environmental conditions.
- Manufacturing: For controlling HVAC in critical production areas.
- Healthcare: For regulating HVAC in hospitals and labs where precise temperature and humidity control is crucial.
12. Can RTUs be retrofitted into existing HVAC systems?
Answer:
Yes, RTUs can often be retrofitted into existing HVAC systems, especially in older buildings. This allows building owners to upgrade their systems with modern remote control and monitoring capabilities without having to replace the entire HVAC infrastructure.

Conclusion
RTUs are a cornerstone of commercial HVAC systems, offering a blend of efficiency, reliability, and scalability. By understanding their basics, working principles, and maintenance needs, you can ensure optimal performance and energy savings. With advancements like smart controls and AI, RTUs are set to remain a vital part of modern HVAC solutions.