Understanding Cooling Systems
Cooling systems are an essential part of modern living, keeping our homes, workplaces, and vehicles comfortable. From scorching summer heat to the need for better air circulation, cooling systems work tirelessly to provide relief and maintain an optimal indoor environment.
In this article, we’ll explore how cooling systems work, delve into their main components, compare central air conditioning and window units, and help you decide which is right for you. Additionally, we’ll share practical tips, hacks, FAQs.
How Cooling Systems Work

At the core, cooling systems operate by removing heat from the air inside a space and releasing it outside. This process involves three main principles:
- Heat Absorption: Refrigerants absorb heat from indoor air as they change from liquid to gas.
- Heat Transfer: The refrigerant transfers the absorbed heat outdoors using a compressor and condenser coil.
- Air Circulation: The cooled air is then circulated back indoors using a fan and ductwork.
Main Components of Cooling Systems
Understanding the basic components of a cooling system can help you maintain it better. Here are the key parts:
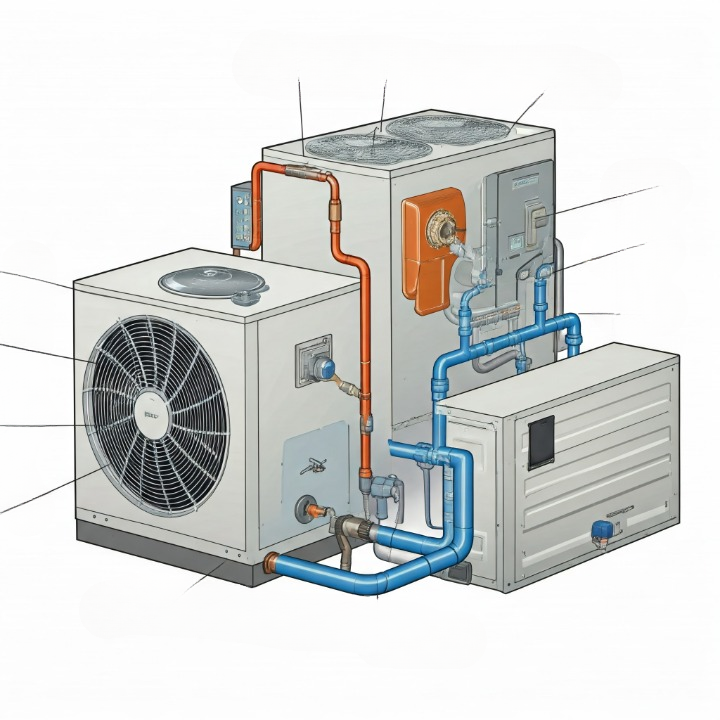
- Compressor: The heart of the system, compressing refrigerant and enabling heat transfer.
- Condenser Coil: Releases heat absorbed from indoors to the outside air.
- Evaporator Coil: Absorbs heat from indoor air, cooling it.
- Refrigerant: A chemical compound that carries heat between indoor and outdoor units.
- Fans: Ensure proper airflow for heat exchange.
- Thermostat: Controls the temperature by regulating the system’s operation.
- Air Filters: Capture dust and debris to ensure clean airflow.
Central Air Conditioning vs. Window Units
Choosing between central air conditioning and window units depends on factors like space, budget, and cooling needs. Here’s a detailed comparison:
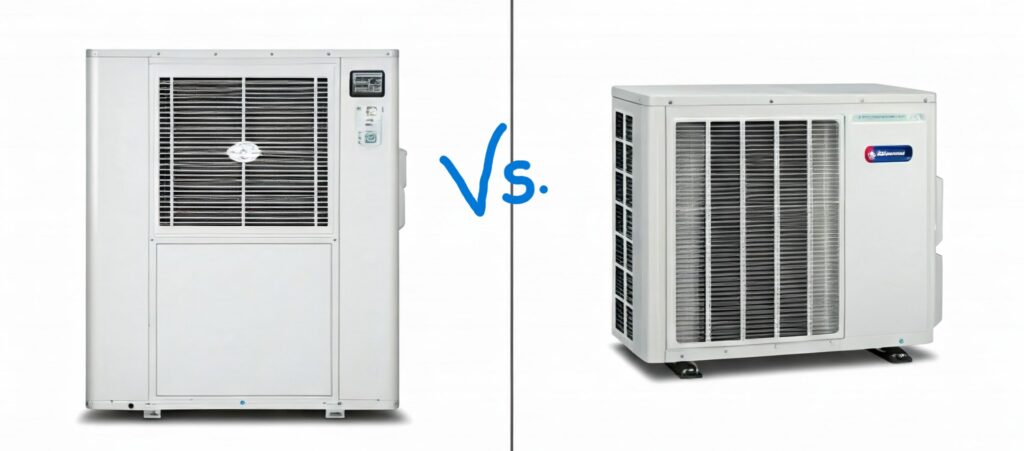

Central Air Conditioning
Pros:
- Cools the entire home evenly.
- Quiet operation as the main unit is outside.
- Improves air quality with advanced filtration.
- Can increase property value.
Cons:
- Higher installation and maintenance costs.
- Requires ductwork.
Window Units
Pros:
- Affordable and easy to install.
- Perfect for small spaces or individual rooms.
- Energy-efficient for targeted cooling.
Cons:
- Noisy operation.
- Less aesthetically pleasing.
- Limited cooling capacity.
Pro Tip: If you’re cooling multiple rooms or a large space, central air conditioning is ideal. For smaller areas or budget-conscious decisions, a window unit works well.
Tips for Cooling Efficiency
- Seal Air Leaks: Ensure doors and windows are sealed to prevent cool air from escaping.
- Clean Filters Regularly: Dirty filters reduce airflow and strain the system.
- Use Programmable Thermostats: Optimize temperature settings when you’re away.
- Shade Outdoor Units: Place the outdoor condenser in a shaded area to improve efficiency.
- Ceiling Fans: Use fans to circulate air and reduce reliance on the cooling system.
- Schedule Maintenance: Annual professional check-ups ensure your system runs smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How often should I service my cooling system?
Ans: It’s recommended to service your system once a year before peak usage seasons.
2. What size cooling system do I need?
Ans: This depends on the size of your space. Consult a professional to calculate the BTU (British Thermal Units) required.
3. Is it normal for cooling systems to run constantly in hot weather?
Ans: Yes, during extreme heat, systems may run longer to maintain desired temperatures.

Conclusion
Whether you choose central air conditioning or a window unit, understanding how cooling systems work and maintaining them effectively can save you money and enhance comfort. With the tips and resources shared here, you’re well-equipped to make an informed decision.