When winter arrives, staying warm and cozy is essential. Choosing the right heating system for your home can make a significant difference in comfort, efficiency, and costs. This guide will explore the most common types of heating systems—furnaces, heat pumps, boilers, radiant heating, and electric heaters. We’ll cover how they work, their pros and cons, tips for maintenance, and FAQs to help you make an informed decision. Plus, you’ll find a free heating system maintenance checklist as a bonus!
Introduction to Heating Systems
Heating systems are a vital part of home comfort. Whether you’re building a new home, renovating, or simply upgrading, understanding your options can save you time and money. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the most popular types:
1. Furnaces: The Most Popular Choice
How Furnaces Work:
Furnaces heat air and distribute it throughout the home via ductwork. They are powered by electricity, natural gas, or oil.
Advantages:
- High efficiency, especially modern models.
- Widely available and relatively affordable.
- Suitable for homes with existing ductwork.
Disadvantages:
- Requires duct maintenance to avoid airflow issues.
- Gas furnaces need regular safety checks.
Pro Tip: Replace furnace filters every 1-3 months during peak usage to maximize efficiency.
Image Tip: Include an image of a modern furnace system installed in a basement.
2. Heat Pumps: Versatile and Energy-Efficient
How Heat Pumps Work:
Heat pumps transfer heat from the outside air or ground to warm your home. They can also function as air conditioners during summer.
Advantages:
- Extremely energy-efficient, especially in mild climates.
- Combines heating and cooling in one unit.
- Environmentally friendly.
Disadvantages:
- Less efficient in extremely cold climates unless paired with a backup system.
- Higher upfront cost.
Hack: Consider a dual-fuel system—pairing a heat pump with a furnace for year-round efficiency.
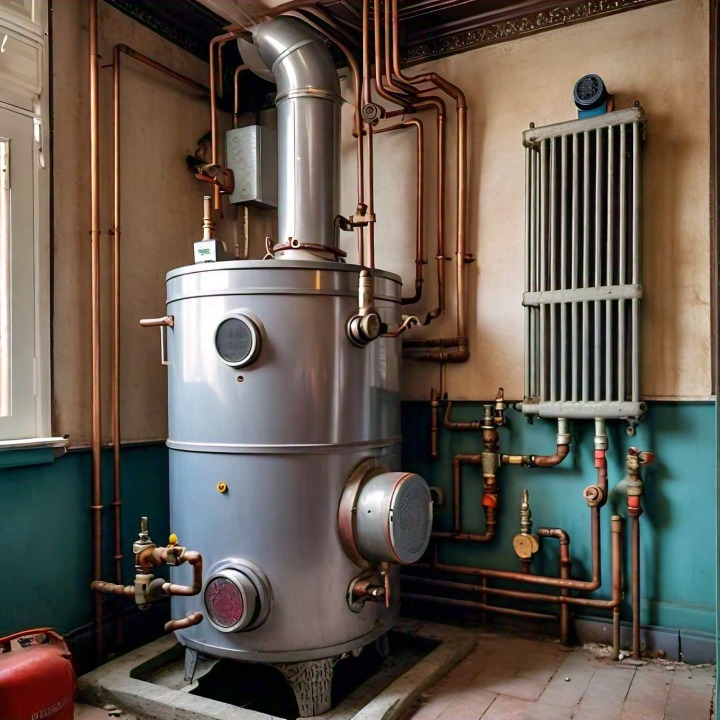
3. Boilers: Efficient and Reliable
How Boilers Work:
Boilers heat water, which is then circulated through pipes to radiators, baseboards, or underfloor systems.
Advantages:
- Provides consistent and even heat.
- No ductwork required, reducing allergen spread.
- Long lifespan with proper maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- Slower to heat up compared to other systems.
- Higher installation costs.
Maintenance Tip: Bleed radiators at the beginning of each heating season to remove trapped air.

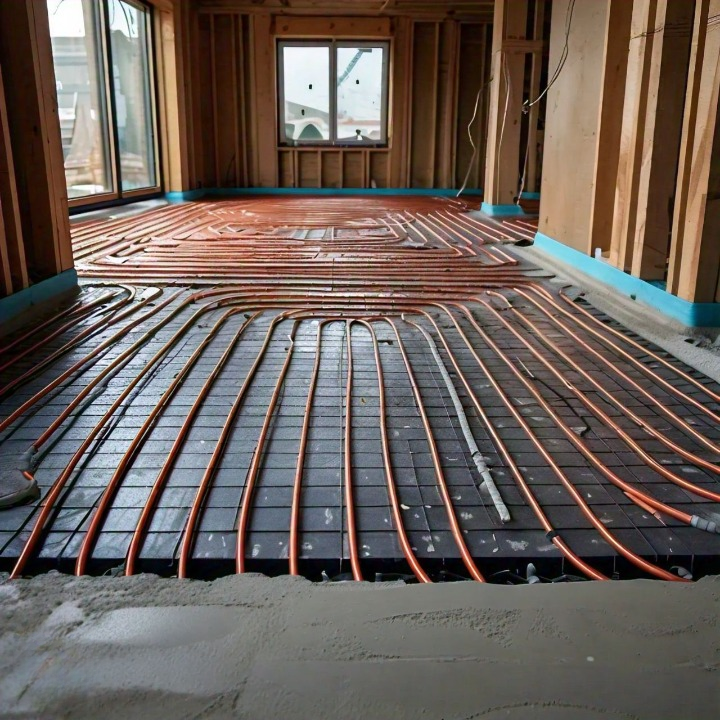
4. Radiant Heating: Luxurious Warmth
How Radiant Heating Works:
Radiant heating involves installing heating elements (water pipes or electric mats) beneath floors or walls to radiate heat.
Advantages:
- Provides uniform and comfortable heat.
- Quiet operation and no visible units.
- Ideal for allergy sufferers as it doesn’t circulate air.
Disadvantages:
- High installation costs.
- Hard to retrofit in existing homes.
Tip: Use a programmable thermostat to maximize energy savings with radiant systems.

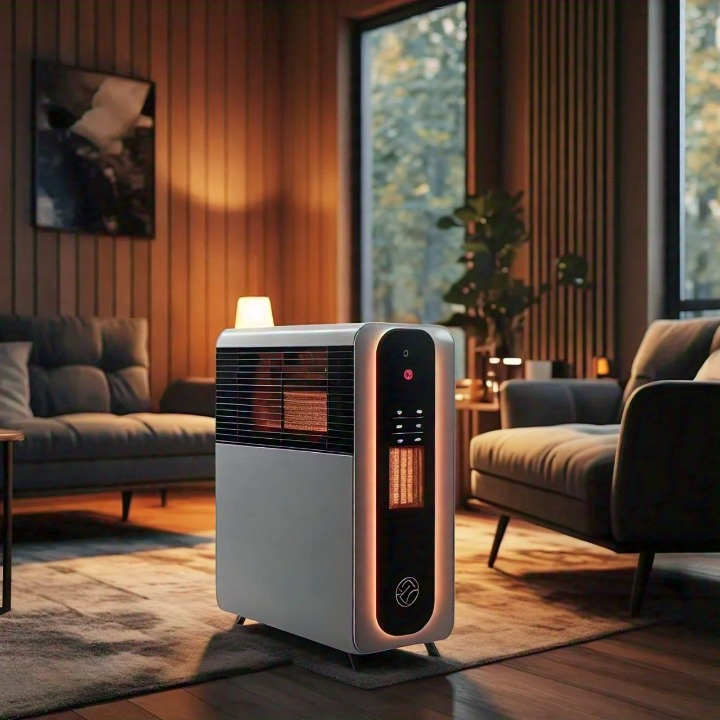
5. Electric Heaters: Affordable and Flexible
How Electric Heaters Work:
Electric heaters use electricity to generate heat, usually through resistance coils. They are available as portable units or permanent installations.
Advantages:
- Low upfront cost.
- Easy to install and use.
- Great for supplemental heating.
Disadvantages:
- High operating costs due to electricity prices.
- Less efficient for whole-home heating.
Hack: Use electric heaters in rooms you occupy the most, and lower the thermostat in other areas.

Tips for Choosing the Right Heating System
- Consider Your Climate: Heat pumps excel in mild climates, while furnaces and boilers are better for colder regions.
- Assess Your Home: Homes with existing ductwork might benefit from furnaces or heat pumps, while radiant heating suits new builds.
- Set a Budget: Evaluate both upfront costs and long-term operating expenses.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for Energy Star-rated systems to save on utility bills.
- Consult a Professional: A heating specialist can assess your needs and recommend the best system.
FAQs
Q: How often should I service my heating system?
A: Ideally, schedule a professional inspection and tune-up annually before the heating season.
Q: Can I use multiple heating systems in one home?
A: Yes, combining systems like radiant heating and a furnace can provide efficient and comfortable heating.
Q: What’s the lifespan of heating systems?
A: Furnaces and boilers last 15-20 years, heat pumps around 10-15 years, and electric heaters about 5-10 years.
Free Bonus: Heating System Maintenance Checklist
Download your free Heating System Maintenance Checklist to keep your system running efficiently and avoid costly repairs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right heating system for your home depends on various factors, including your budget, climate, and personal preferences. From efficient heat pumps to luxurious radiant heating, understanding these systems will help you make a smart investment in your comfort.
Stay warm and cozy this winter, and don’t forget to grab your free maintenance checklist!